The head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid In addition, both muscles workingThe pain in the back of your head occurs when one or a combination of factors affect your brain The Mayo Clinic says that these factors can be chemical activity in your brain, the nerves of blood vessels surrounding your skull, or the muscles at the back of the head and neck 1 Also, some people are more prone to headaches than others Knowing what causes headaches can help you know how toHuman head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of mastication
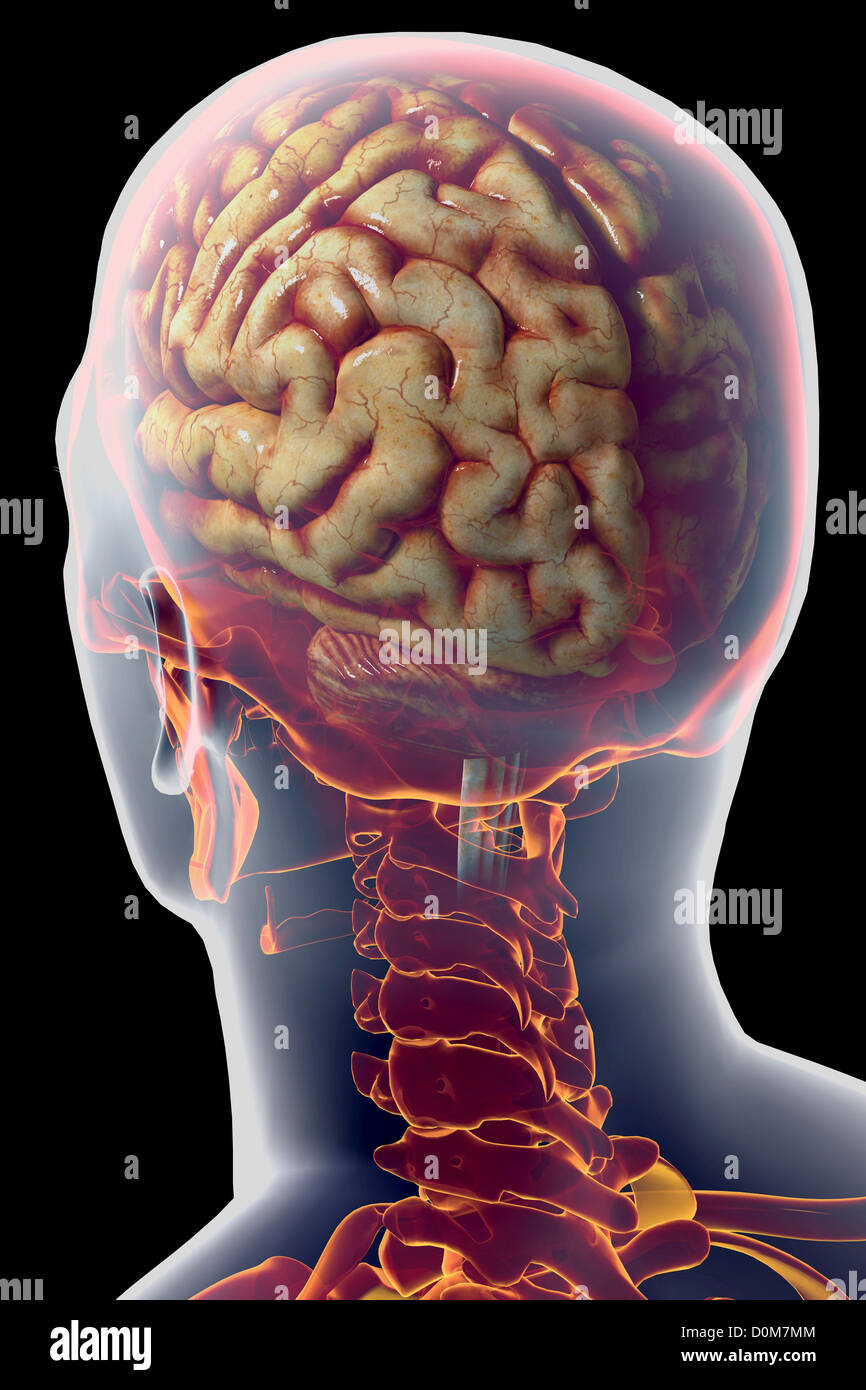
Rear Three Quarter View Of The Human Brain Within The Skull Stock Photo Alamy
Human back head structure
Human back head structure-Head and neck anatomy focuses on the structures of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves in a newborn, the junction of the paritial bones with the frontal and occipital bones, form the anterior (front) and posterior (back) fontanelle, or soft spotsFemale Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration Illustration of muscle, meat from thumbsdreamstimecom Vector cartoon illustration of human muscular system for kids Short of a great deal of descriptive text, the easiest way to answer this is with illustrations



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Anatomyinsider
Mucus may drip down the back of your throat warm air to collect by draping a towel over your head as you lean over the bowl Understand your individual sinus anatomyThe occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the cranium bonesHuman Back Of Neck Anatomy The bones of the head and neck AnatomyMedicineCOM Anatomy for plastic surgery of the face, head, and neck details the complex regional anatomy They reach the eye via three holes located at the back wall of the orbit The back comprises the spine and spinal nerves, as well as several different muscle groups
New users enjoy 60% OFF 156,731,624 stock photos onlineFemale Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration Illustration of muscle, meat from thumbsdreamstimecom Vector cartoon illustration of human muscular system for kids Short of a great deal of descriptive text, the easiest way to answer this is with illustrationsThe bones of the head form a protective cavity around the brain The bones of the head meet at joint lines called sutures They are a type of fibrous joint, which are immovable The 22 bones of the skull can be divided in to two main categories the cranium and the facial skeleton
Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jaw It is attached to the spinal column by way of the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, and connected with the trunk of the body by the muscles, blood vessels, and nerves that constitute the neckThe skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain It is comprised of many bones, which are formed by intramembranous ossification, and joined by sutures (fibrous joints) The bones of the skull can be considered as two groups those of the cranium (which consist of the cranial roof and cranial base) and those of the faceHead Head includes face and cranium ADVERTISEMENTS Surface land marks (Fig 151) External occipital protruberance It can be felt as a palpable projection at the upper end of the nuchal furrow on the back of neck Inion ADVERTISEMENTS Is the highest
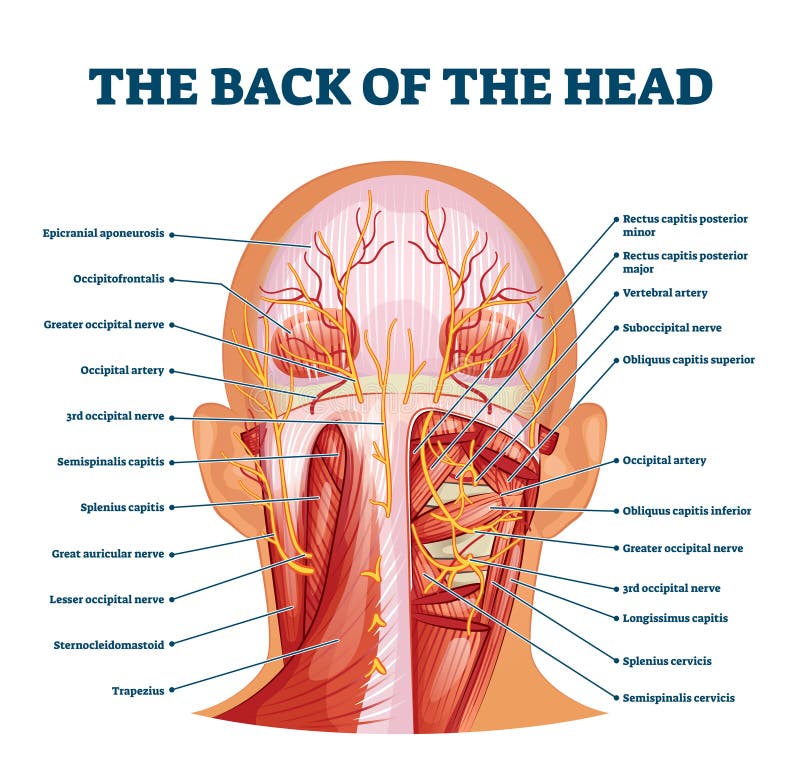


Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle
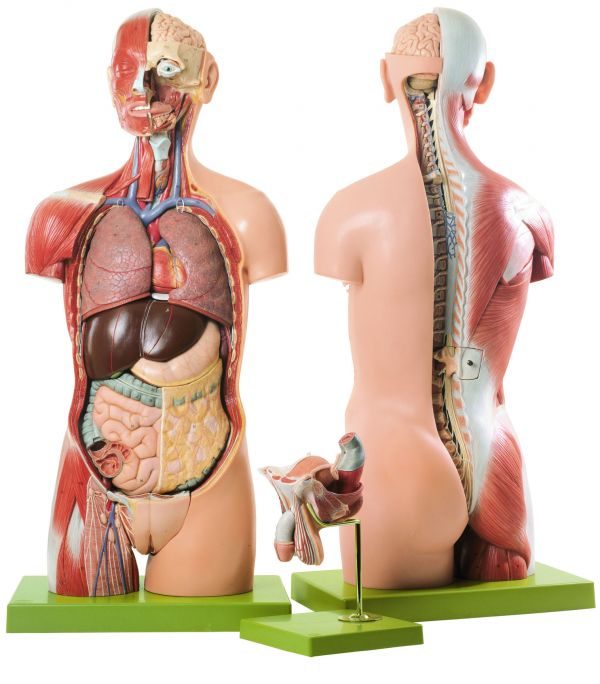


Somso Torso With Head And Open Back
The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at C1 (the first cervical vertebra known as the atlas) The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine The skull can be further subdivided intoThe occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the cranium bonesThe bones of the head form a protective cavity around the brain The bones of the head meet at joint lines called sutures They are a type of fibrous joint, which are immovable The 22 bones of the skull can be divided in to two main categories the cranium and the facial skeleton



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Anatomyinsider
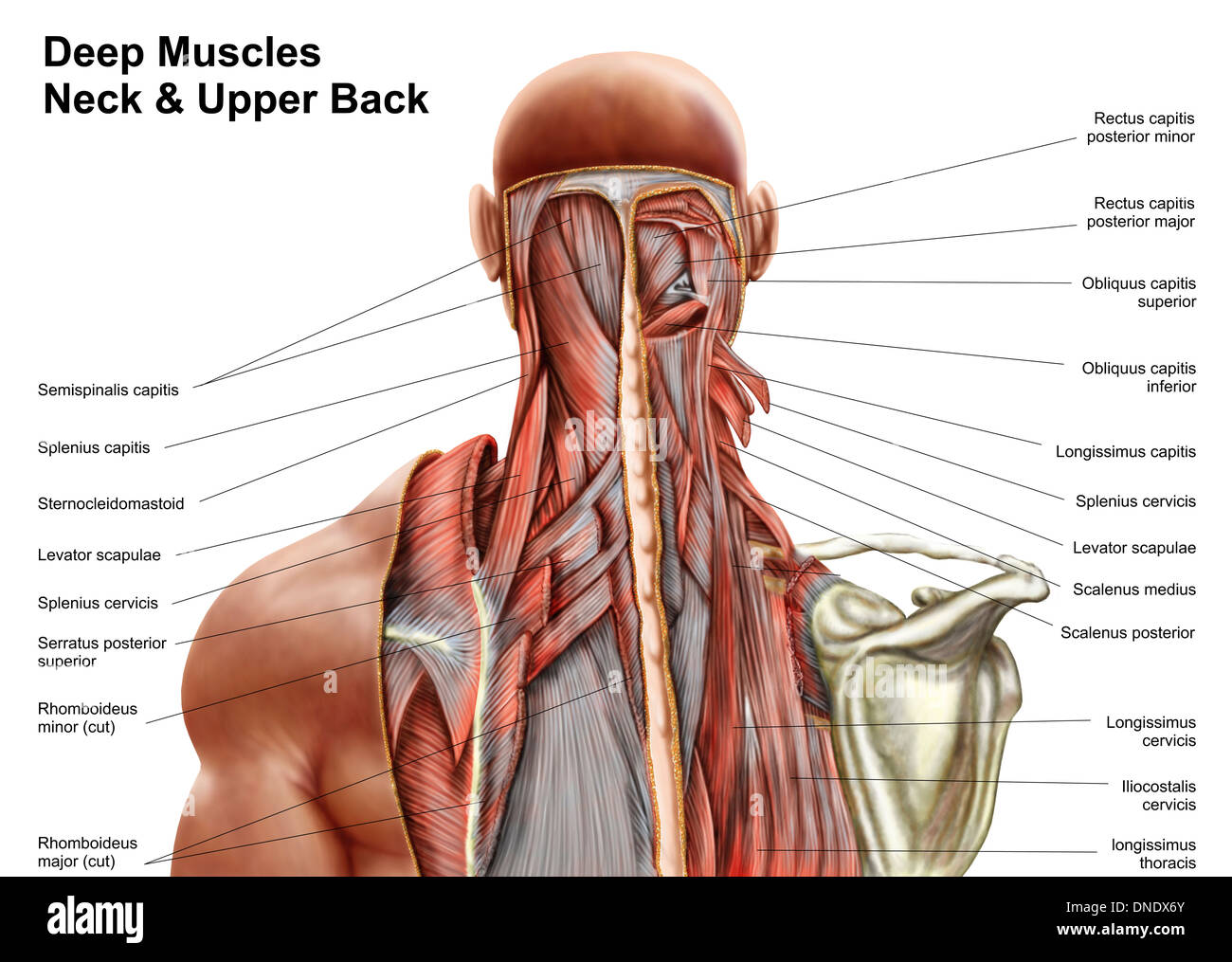


Human Anatomy Showing Deep Muscles In The Neck And Upper Back Stock Photo Alamy
Body parts Human anatomy head legs fingers nose hands back belly vector fragments collection Back and head human, foot and hand illustration Files in package — EPS, vector file for Adobe Illustrator or import into Photoshop — JPG in High ResolutionBack anatomy Bones, nerves, and conditions The cervical spine protects the nerves connecting to the brain, allowing the head to move freely while supporting its weightDownload 172 Man Body Anatomy Front Back Side Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart for FREE or amazingly low rates!



Muscles Of The Head Neck Anatomy Model Youtube



Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information
Back muscles are arranged in several layers, so they are divided into deep and superficial, which, in turn, are arranged in two layers By the middle line of the back is a longitudinal groove back (sulcus dorsi) Along it are easily palpable spinous processes by palpation of the cervical VII and all lying below the vertebraeADVERTISEMENTS Here are your notes on the surface Anatomy of Head and Neck!The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at C1 (the first cervical vertebra known as the atlas) The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine The skull can be further subdivided into



Head Anatomy Human Head Brain Anatomy Watercolor Brain Iphone Case Cover By Rosaliartbook Redbubble



Human Head Anatomy Drawing Anatomy Front And Back Hd Png Download Transparent Png Image Pngitem
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Head And Neck Muscles DiagramWe hope this picture Head And Neck Muscles Diagram can help you study and research for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website wwwanatomynotecom Anatomynotecom found Head And Neck Muscles Diagram from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internetDownload Back anatomy stock photos Affordable and search from millions of royalty free images, photos and vectors human body anatomy, vector man front back side Vector Similar Images Add to Likebox Both hips joint xray showing destruction head right femur and Similar Images Add to Likebox # Lower back painHuman Head Surface Anatomy Outline Front, back, top and profile views of the surface anatomy of the human head in outline Includes EPS, AI CS2 and hires JPG human head stock illustrations Human head
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12652/Introduction.png)


Nerves And Arteries Of Head And Neck Anatomy Branches Kenhub



Head Definition Anatomy Britannica
The human back, also called the dorsum, is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomenThe vertebral column runs the length of the back and creates a central area of recession The breadth of the back is created by the shoulders at the top and the pelvis at the bottomHuman Back Of Neck Anatomy The bones of the head and neck AnatomyMedicineCOM Anatomy for plastic surgery of the face, head, and neck details the complex regional anatomy They reach the eye via three holes located at the back wall of the orbit The back comprises the spine and spinal nerves, as well as several different muscle groupsHead and neck anatomy focuses on the structures of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves in a newborn, the junction of the paritial bones with the frontal and occipital bones, form the anterior (front) and posterior (back) fontanelle, or soft spots



Human Head Anatomy Jigsaw Puzzle Genius Games



The Artist S Guide To The Anatomy Of The Human Head Defining Structure And Capturing Emotions 3dtotal Publishing Amazon Com Books
The back anatomy includes the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, erector spinae, rhomboid, and the teres major On this page, you'll learn about each of these muscles, their locations and functional anatomy Function of the Back Muscles There are several individual muscles within the back anatomy, and it's important to take a quick look at all ofThe vertebral bodies of the lower back are the largest of the spine and they bear the majority of the body's weight See Lumbar Spine Anatomy and Pain Approximately 50% of flexion (bending forward) occurs at the hips, and 50% occurs at the lumbar spine (lower back) Each segment of the lumbar spine is comprised of the following structuresThe lumbar region of the spine, more commonly known as the lower back, is situated between the thoracic, or chest, region of the spine, and the sacrum Watch Lumbar Spine Anatomy Video Understanding the anatomy of your lower spine can help you communicate more effectively with the medical professionals who treat your lower back pain



Drawing The Human Head Anatomy Expressions Emotions And Feelings Colombo Giovanni Vigliotti Giuseppe Amazon Com Books
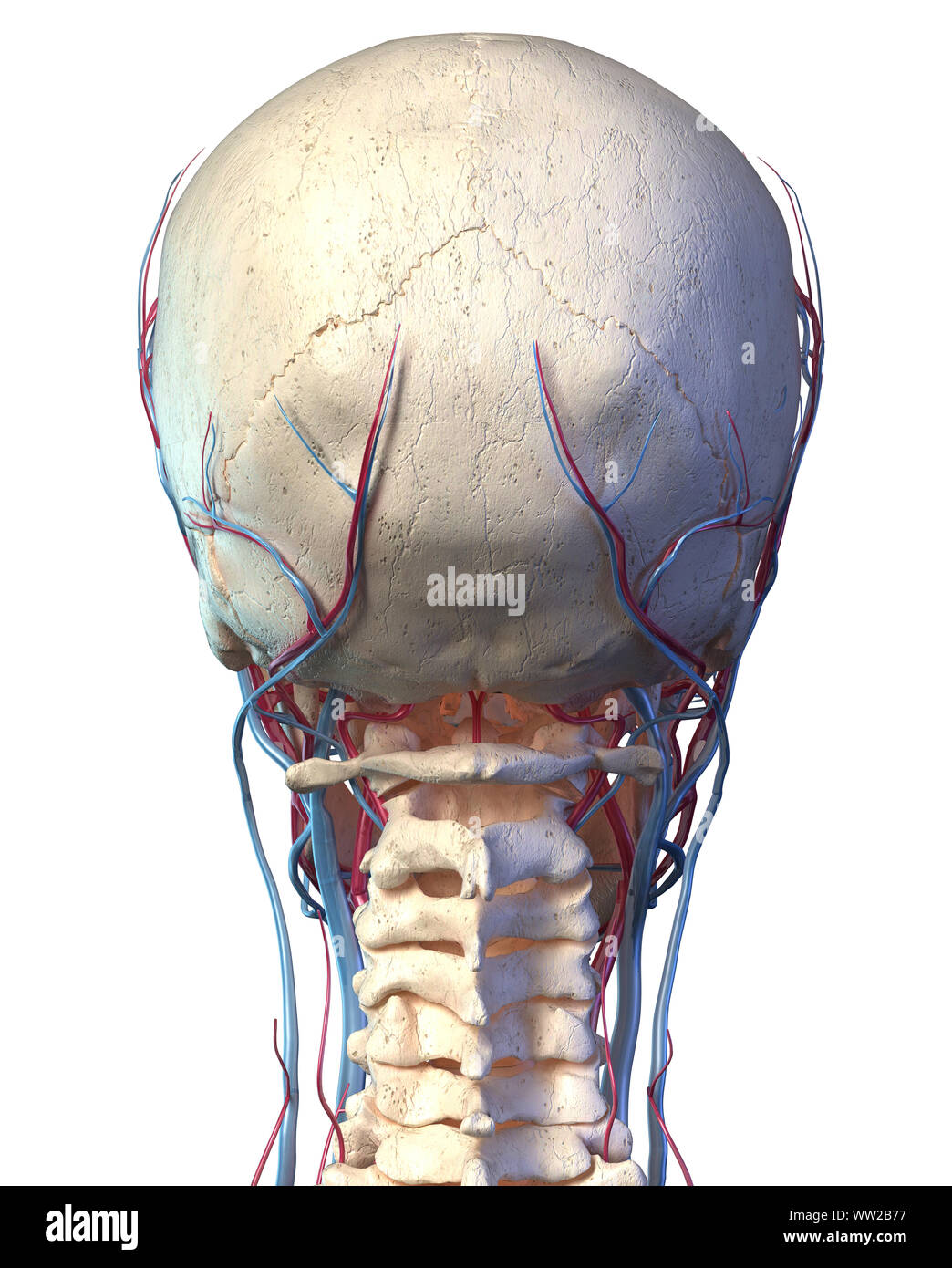


Vascular System Of The Human Head Viewed From The Back Computer 3d Rendering Artwork On White Background Stock Photo Alamy
Starting from the top of the head—the brightest area—the head gets progressively darker as the planes turn from the light to the back of the head This subtle value shift produces the look of a rounded structure D Try drawing the head in simple planes in a variety of positions Remember to leave out details—eyes, eyebrows, nostrils and• The external carotid artery is divided into branches (facial, temporal and occipital arteries) which supply the skin and muscles of the face, side and back of the head respectively This vessel also supplies more superficial parts and structures of the head and neckThe muscles of the head and neck perform many important tasks, including movement of the head and neck, chewing and swallowing, speech, facial expressions, and movement of the eyes These diverse tasks require both strong, forceful movements and some of the fastest, finest, and most delicate adjustments in the entire human body


Hb Anatomy Skull
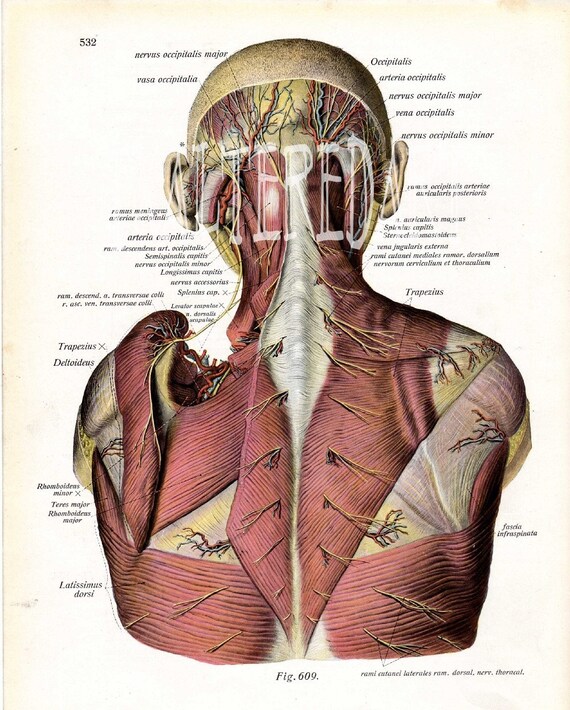


1934 Human Anatomy Vintage Book Illustration Back Head Anatomy Etsy
The occipital glands (lymphoglandulæ occipitales), one to three in nu ber, are placed on the back of the head close to the margin of the Trapezius and resting on the insertion of the Semispinalis capitisTheir afferent vessels drain the occipital region of the scalp, while their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical glands The posterior auricular glands (lymphoglandulæ auricularesThe human head consists of a fleshy outer portion, which surrounds the bony skullThe brain is enclosed within the skull There are 22 bones in the human head The head rests on the neck, and the seven cervical vertebrae support it The human head typically weighs between 23 and 5 kilograms (51 and 110 lb)Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jaw It is attached to the spinal column by way of the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, and connected with the trunk of the body by the muscles, blood vessels, and nerves that constitute the neck



Anatomy Massage Therapy Anatomy Migraine



Human Head Brain And Spinal Column Rear View Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
Using this atlas of human anatomy of the spine and back On "Anatomical parts" the user can choose to display the various structures in colored illustrations of the anatomy of the back and spine vertebrae, bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, muscular system, fascia, arteries, veins, nerves and various adjacent organsFemale Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration Illustration of muscle, meat from thumbsdreamstimecom Vector cartoon illustration of human muscular system for kids Short of a great deal of descriptive text, the easiest way to answer this is with illustrationsThe skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain It is comprised of many bones, which are formed by intramembranous ossification, and joined by sutures (fibrous joints) The bones of the skull can be considered as two groups those of the cranium (which consist of the cranial roof and cranial base) and those of the face



65 581 Human Head High Res Illustrations Getty Images



Human Head Back Side Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Human Anatomy
The head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid In addition, both muscles workingHead and neck anatomy focuses on the structures of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves in a newborn, the junction of the paritial bones with the frontal and occipital bones, form the anterior (front) and posterior (back) fontanelle, or soft spotsHead and neck (anterior view) The head and neck are two examples of the perfect anatomical marriage between form and function, mixed with a dash of complexity The neck is resilient enough to sustain a five kilogram weight 24/7, yet sufficiently mobile to move it in several directions



Anatomy Head Back Google Search Anatomy Photo Movie Posters



Muscles And External Anatomy Of The Human Head Case Skin For Samsung Galaxy By Taylorcustom Redbubble
Back muscles are arranged in several layers, so they are divided into deep and superficial, which, in turn, are arranged in two layers By the middle line of the back is a longitudinal groove back (sulcus dorsi) Along it are easily palpable spinous processes by palpation of the cervical VII and all lying below the vertebraeHead and neck anatomy focuses on the structures of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves in a newborn, the junction of the paritial bones with the frontal and occipital bones, form the anterior (front) and posterior (back) fontanelle, or soft spotsHead hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such an
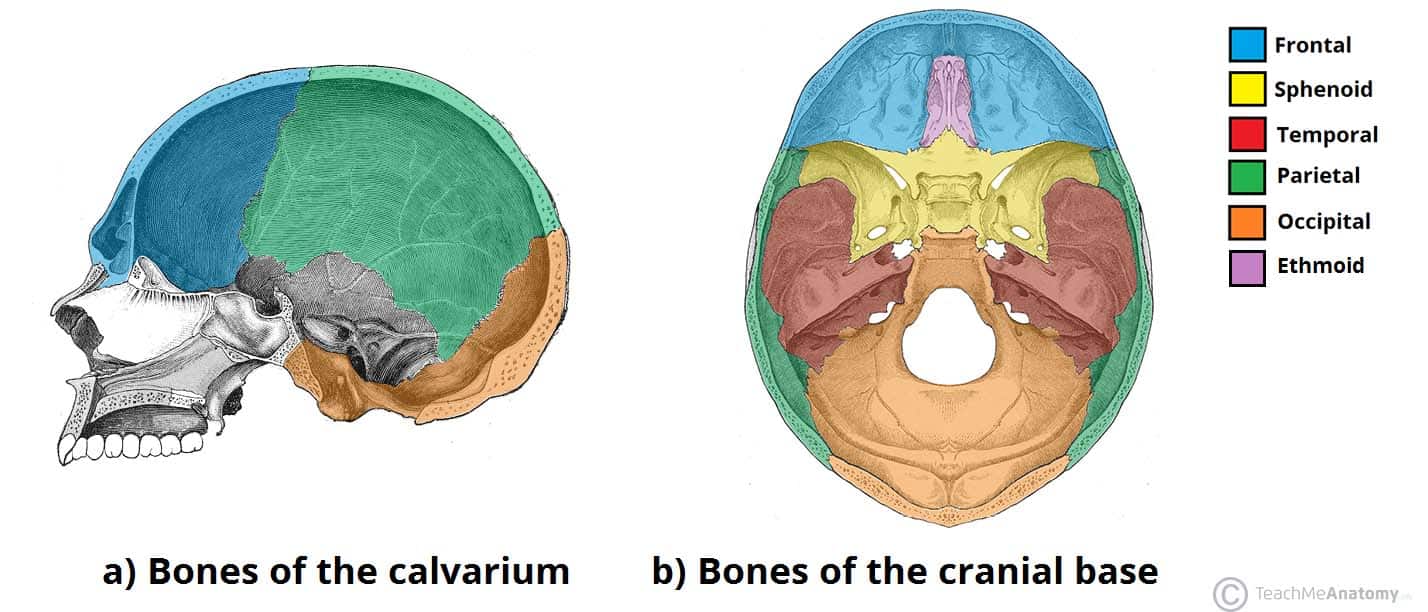


Bones Of The Skull Structure Fractures Teachmeanatomy



Neck Anatomy Britannica
The human head consists of a fleshy outer portion, which surrounds the bony skullThe brain is enclosed within the skull There are 22 bones in the human head The head rests on the neck, and the seven cervical vertebrae support it The human head typically weighs between 23 and 5 kilograms (51 and 110 lb)The head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid In addition, both muscles workingIn addition to housing main parts of the nervous system — the brain and spine — and the start of the digestive system, the head contains many important sensory organs



Anatomy Of Muscles Of Head Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
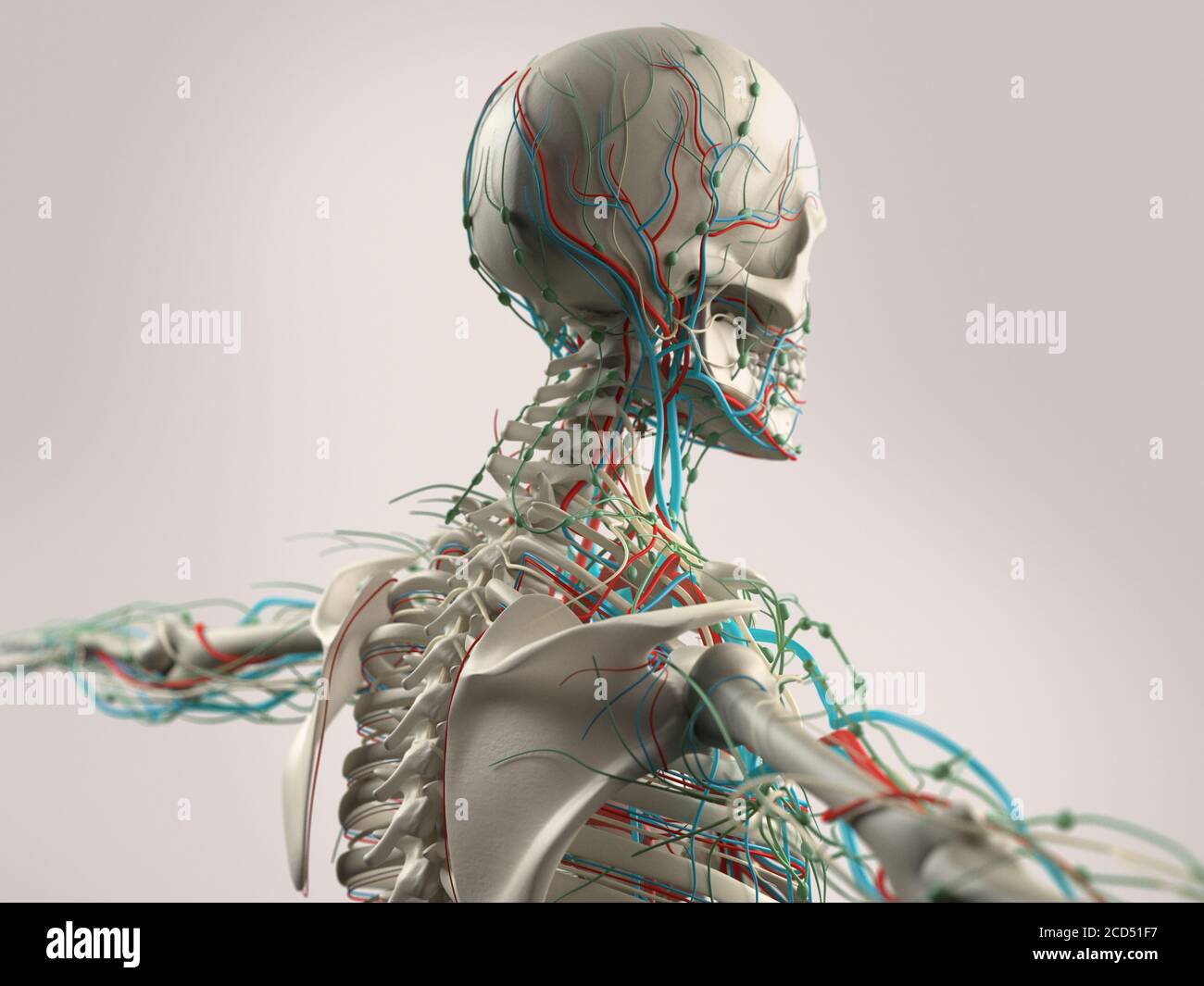


Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Muscular System Bone Structure And Vascular System Stock Photo Alamy
Structure Bones The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at C1 (the first cervical vertebra known as the atlas)The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine The skull can be further subdivided intoThe head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid In addition, both muscles workingSimply stated, human anatomy is the study of the parts of the human body Human anatomy includes both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy Gross anatomy includes those human structures that can be seen with the naked eye Gross anatomy can be compared to the structure of a house as shown in a blueprint of a house or by looking at and
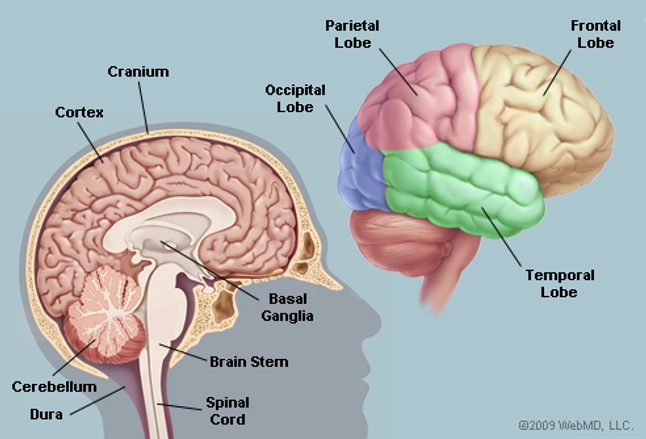


Brain Human Anatomy Picture Function Parts Conditions And More
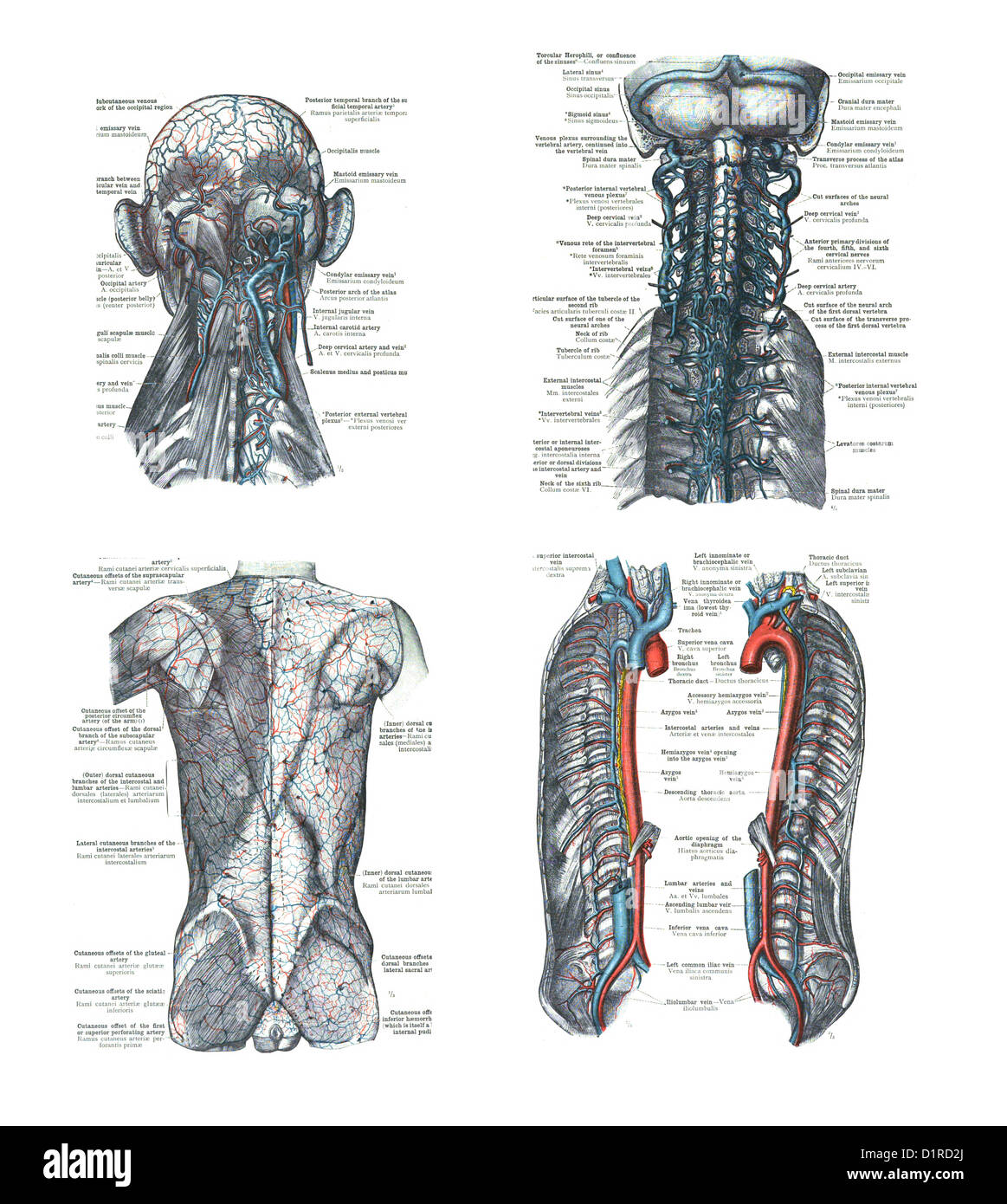


4 Views Of The Human Head Spine And Back An Atlas Of Human Anatomy Stock Photo Alamy
Head hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such an



Human Anatomy Human Brain Front Back Stock Vector Royalty Free



Human Body Skull Anatomy External Occipital Protuberance Human Back Of Skull Face Human Png Pngegg
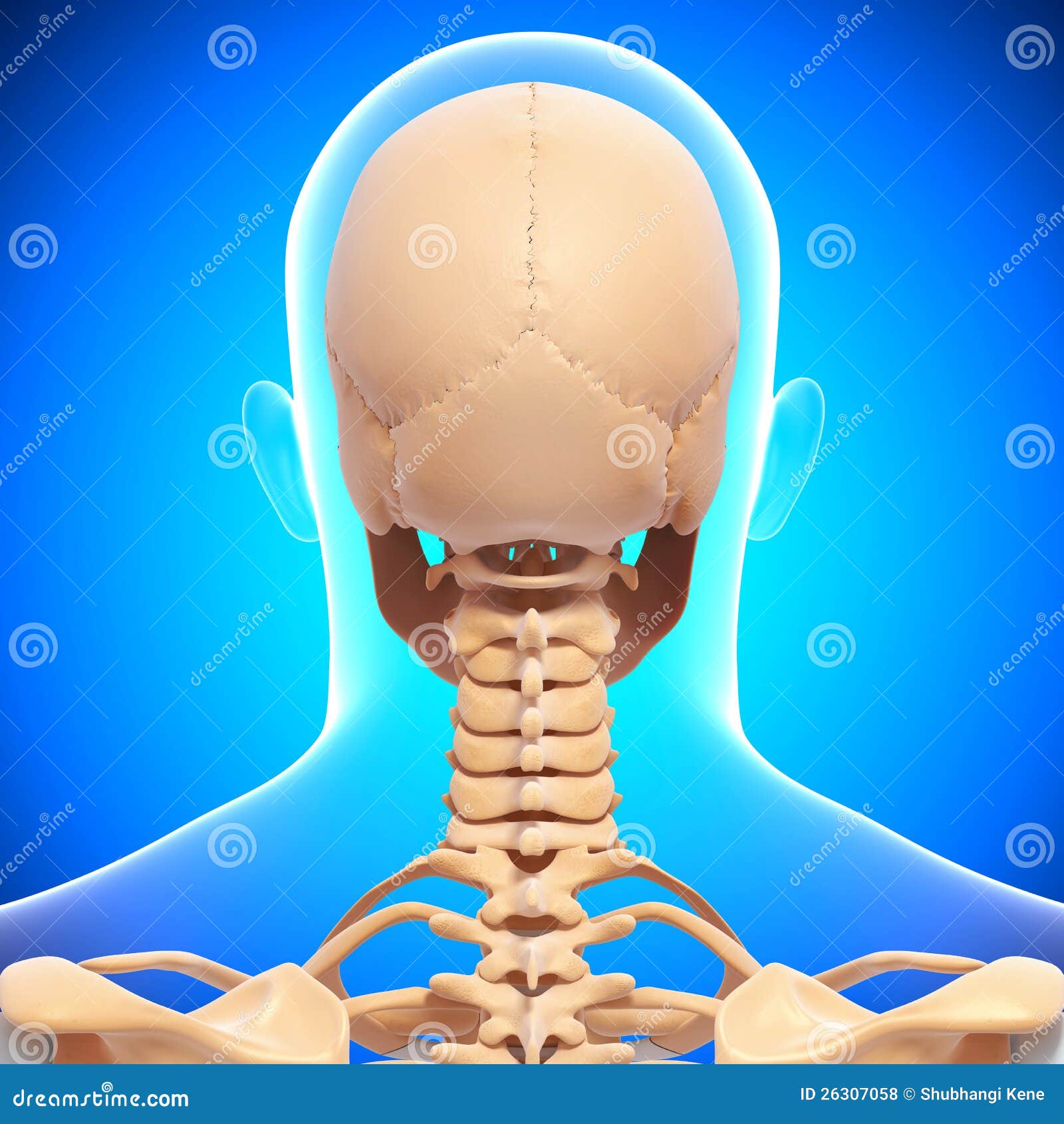


Human Head Skeleton In Blue Stock Illustration Illustration Of Apex Pulmonary



Human Head Neck Skull Anatomy Medical Anatomical Chart Educationalmodel Com Amazon Com Books



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Anatomyinsider



Anatomy Back View Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo C Anatomyinsider



Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Muscle Human Body Latissimus Dorsi Hand Human Head Png Pngwing
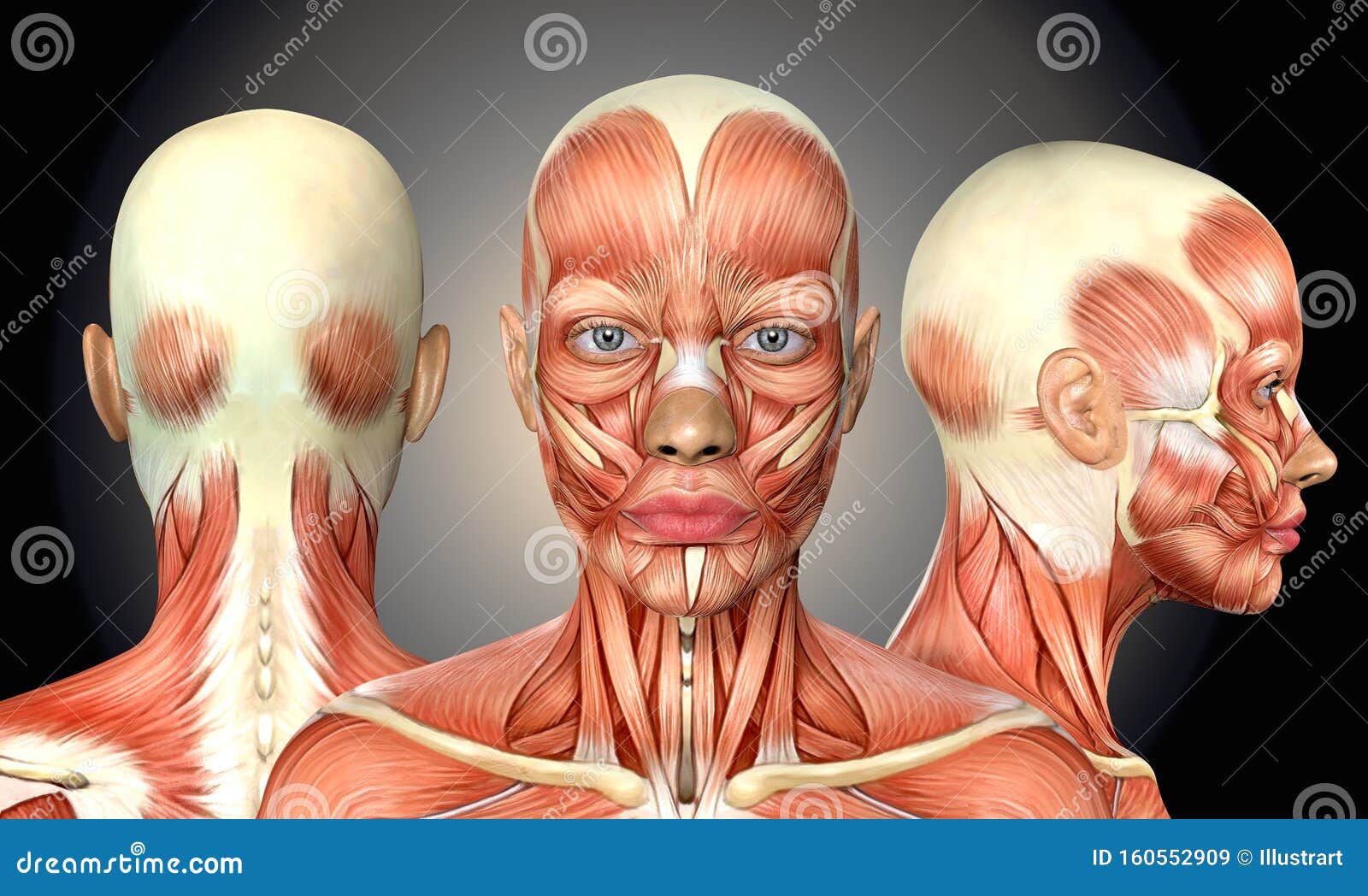


3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy With Front Back And Side View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Exercise Female



Face Wikipedia



Back Head Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram
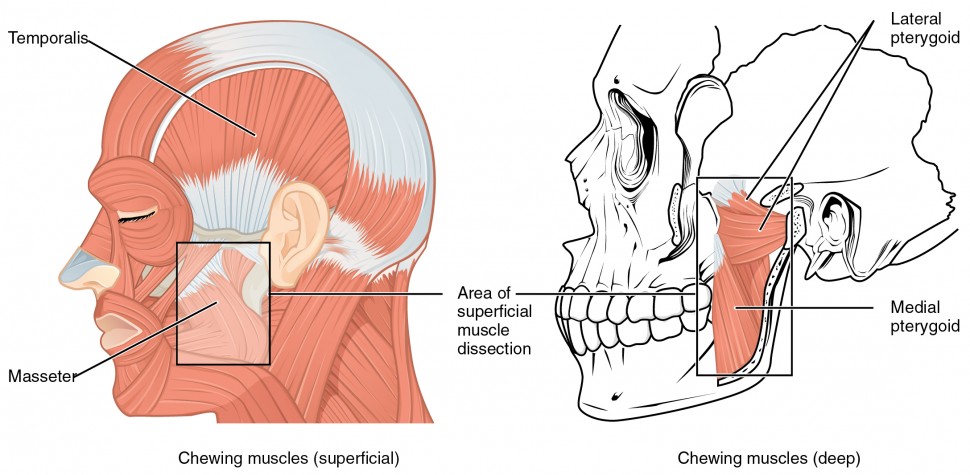


Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I


3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Deryadraws



Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing



Very Detailed And Scientifically Correct Human Skull Back View Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image



Human Head Anatomy Stock Illustration K Fotosearch
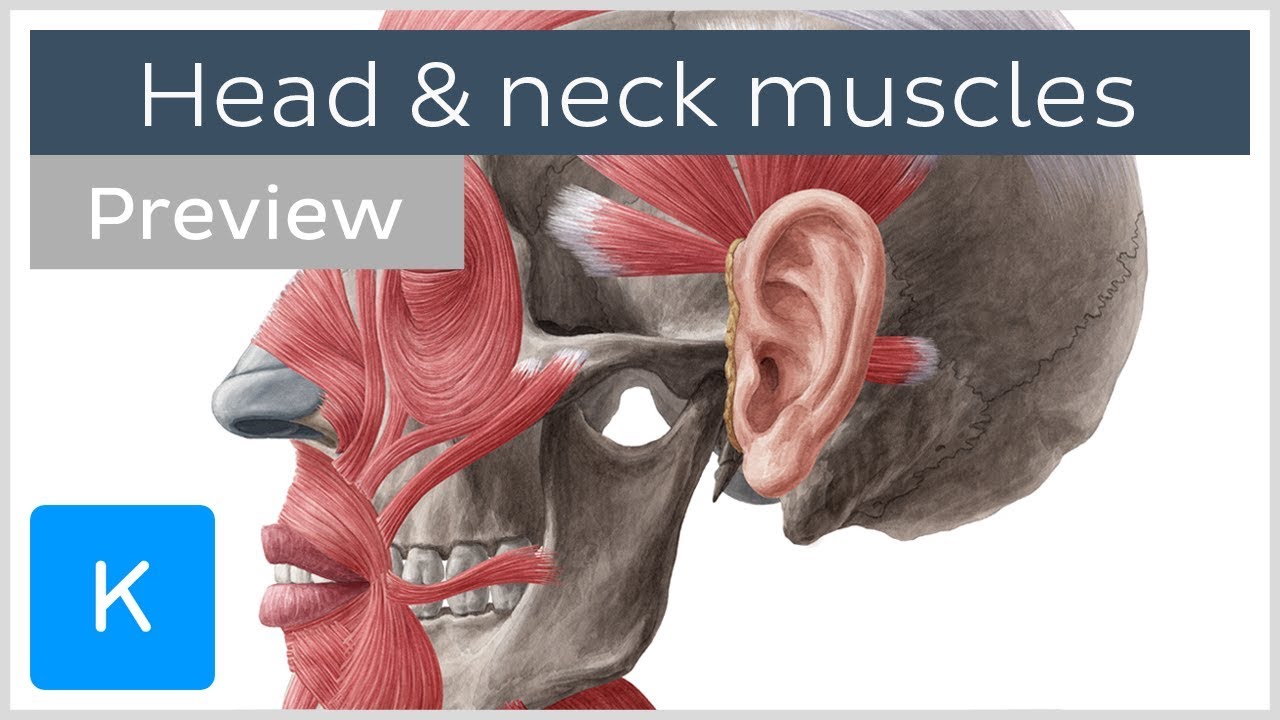


Main Muscles Of The Head And Neck Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10606/Head_Thumbnail__1_.png)


Head Anatomy Muscles Glands Arteries And Nerves Kenhub



Head Muscles Diagram Koibana Info Head Muscles Face Muscles Anatomy Muscle Diagram
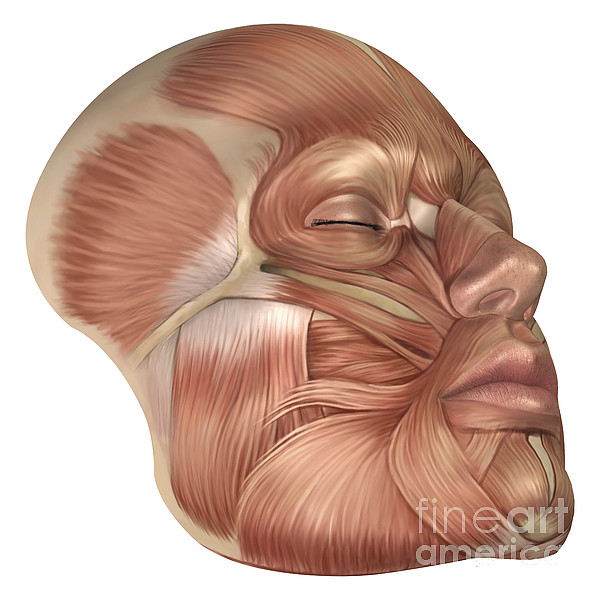


Anatomy Of Human Face Muscles Tote Bag For Sale By Stocktrek Images



Human Head Wikipedia



Female Head Muscles Anatomy Side View Head Anatomy Human Skull Anatomy Head Muscles



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo C Anatomyinsider



Pin By Kayla Sims On Anatomy Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscle Anatomy Human Anatomy
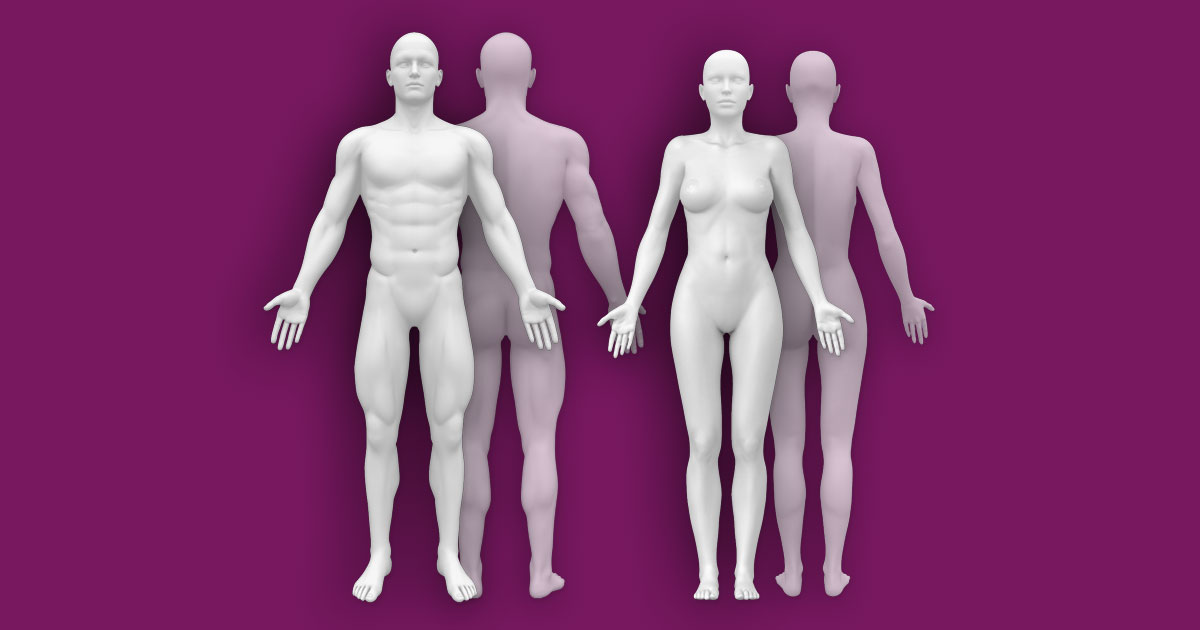


Interactive Human Anatomy Figure Male Female Front Back
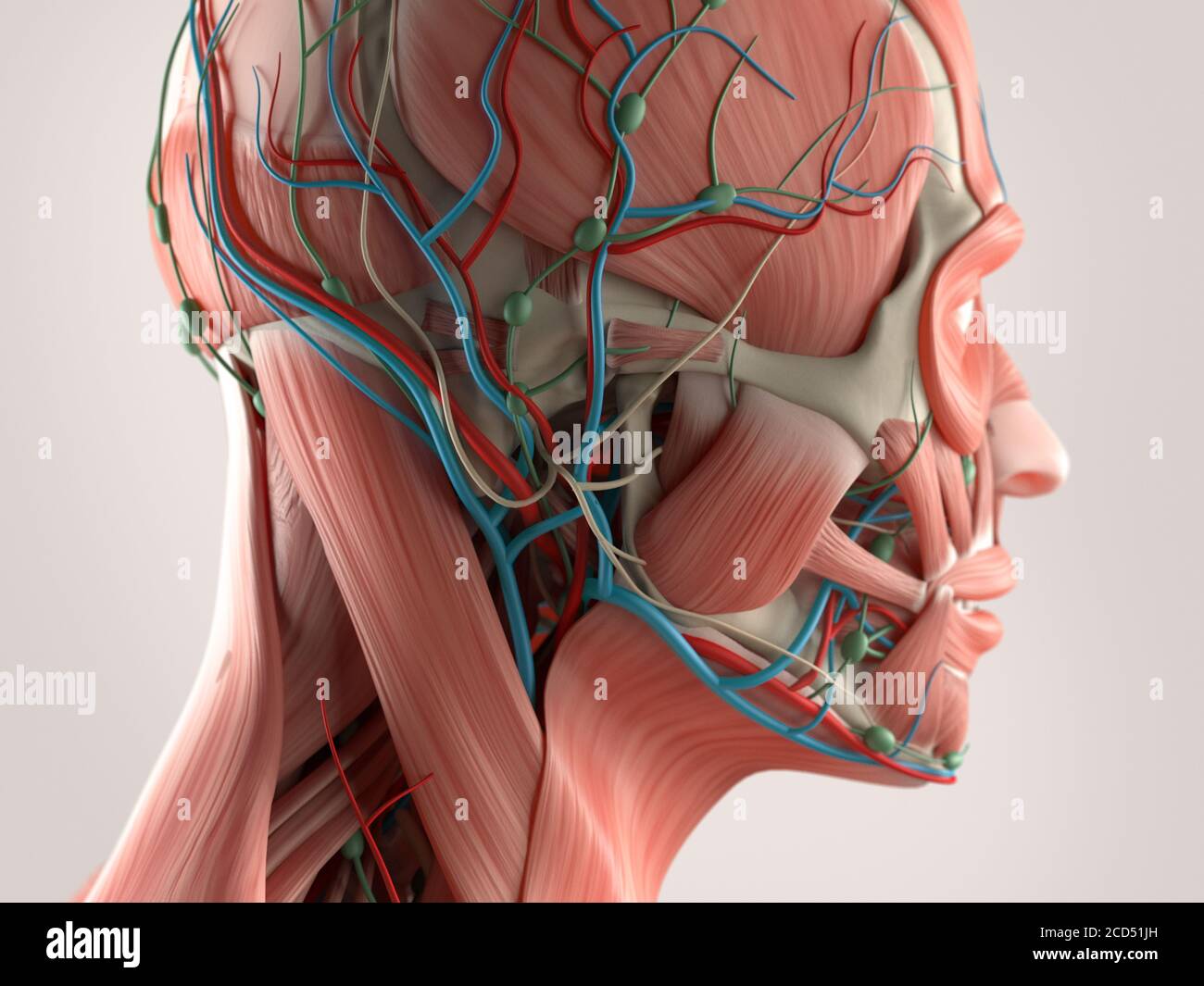


Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Muscular System Bone Structure And Vascular System Stock Photo Alamy



Rear Three Quarter View Of The Human Brain Within The Skull Stock Photo Alamy



Human Head Skull Anatomy 3d Illustration Rear View On Black Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image



Bones Of The Head And Neck Skull And Cervical Spine Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube



Neck Anatomy Britannica



Human Anatomy Skeletal System Of The Torso Viewed From The Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image



Respiratory Half Head Anatomy Youtube
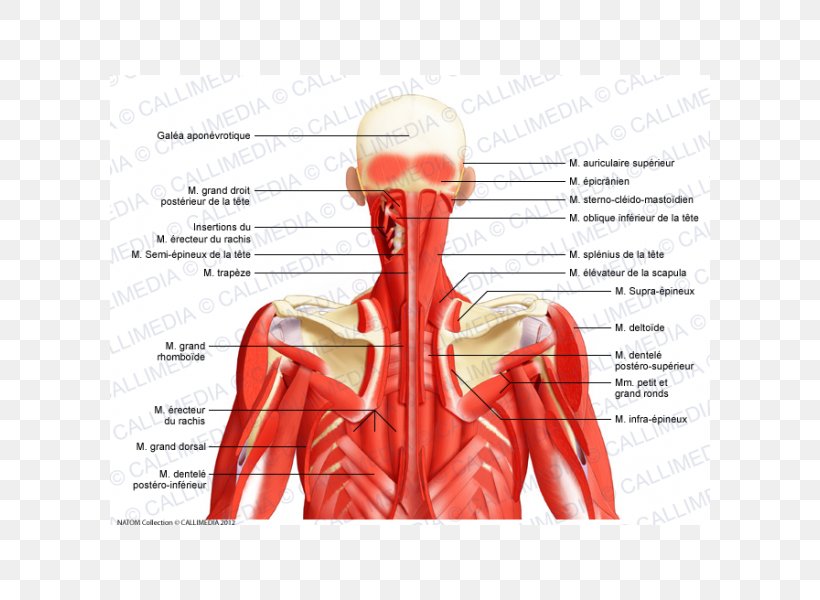


Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human Body Muscle Png 600x600px Watercolor Cartoon
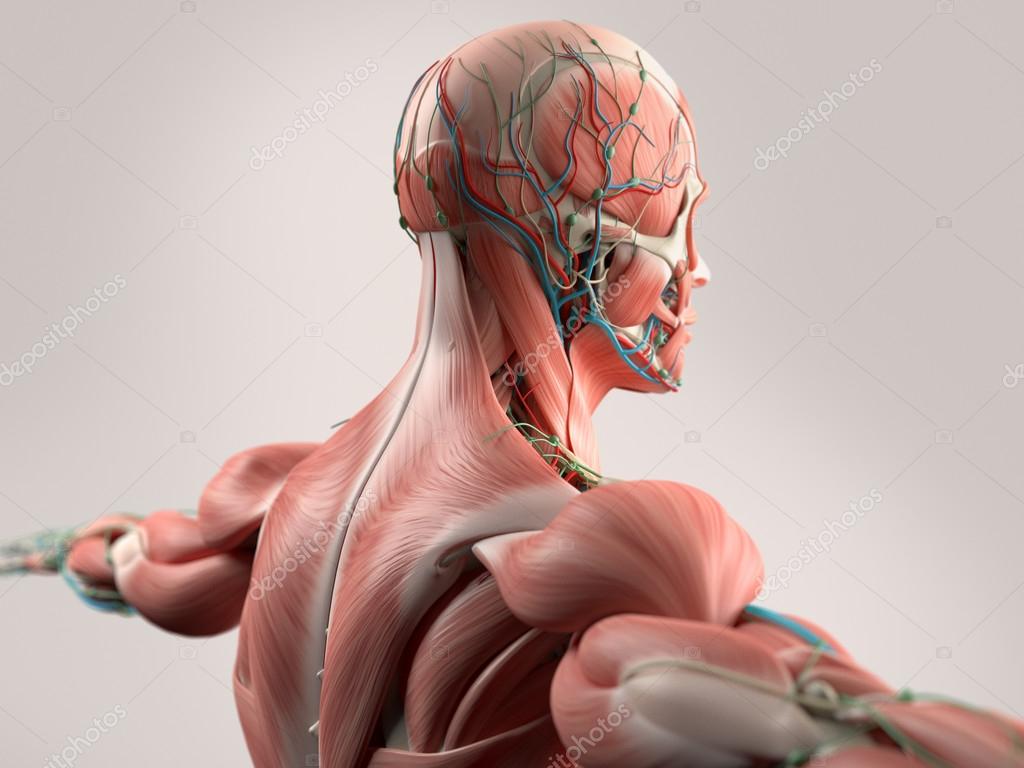


Picture Back Muscles And Bones Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Muscular System Bone Structure And Vascular System Stock Photo C Anatomyinsider



Human Back Human Head Human Body Muscle Others Head Human Anatomy Png Pngwing



Back Of Head Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Human Anatomy Openstax Cnx



Anatomy Of Back Of Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram



3d Rendered Illustration Of Human Head Anatomy Back View Canstock
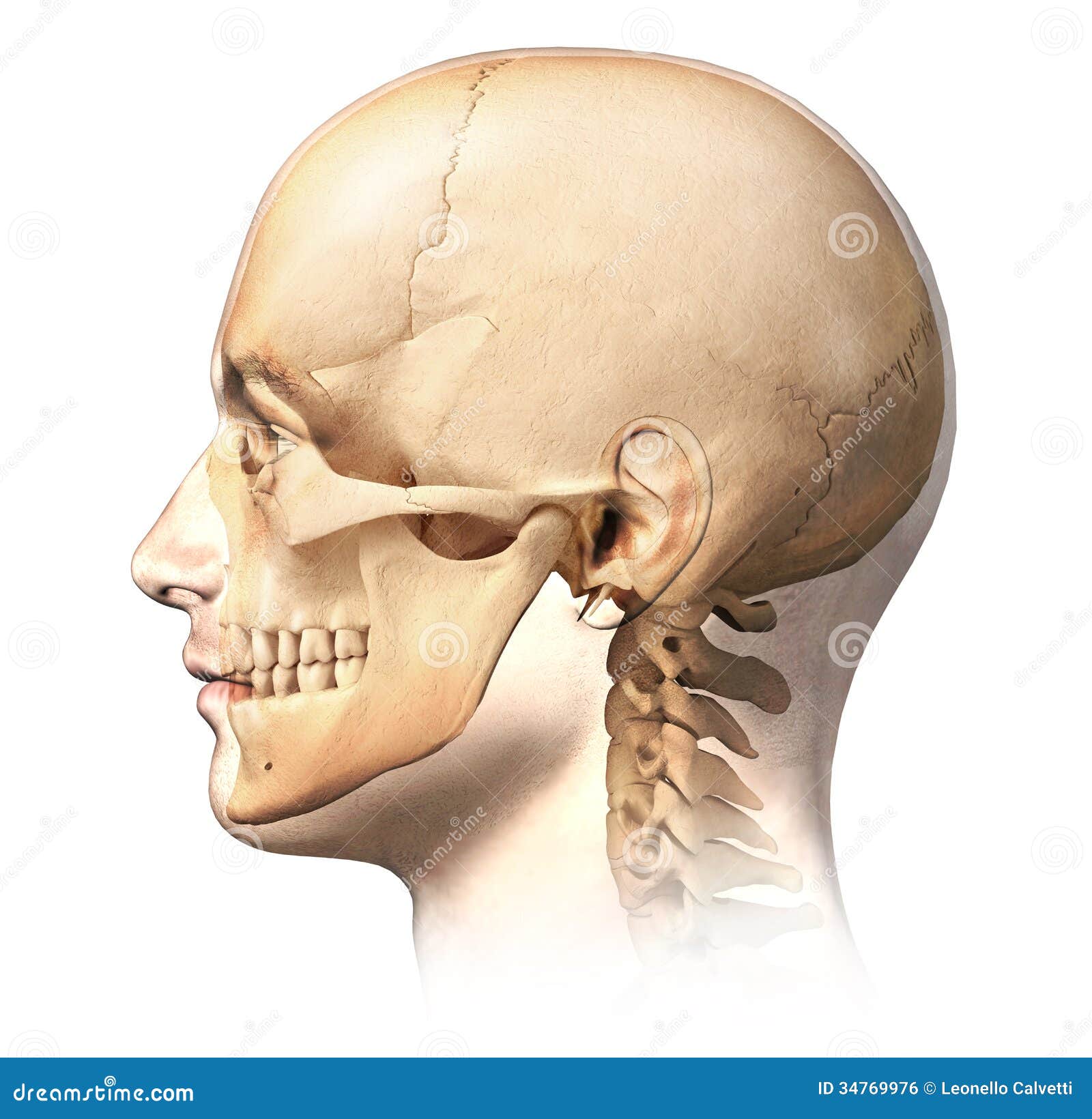


Male Human Head With Skull In Ghost Effect Side View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Inside Human



Human Skull 3 4 Back View Skull Reference Human Skull Skull Anatomy
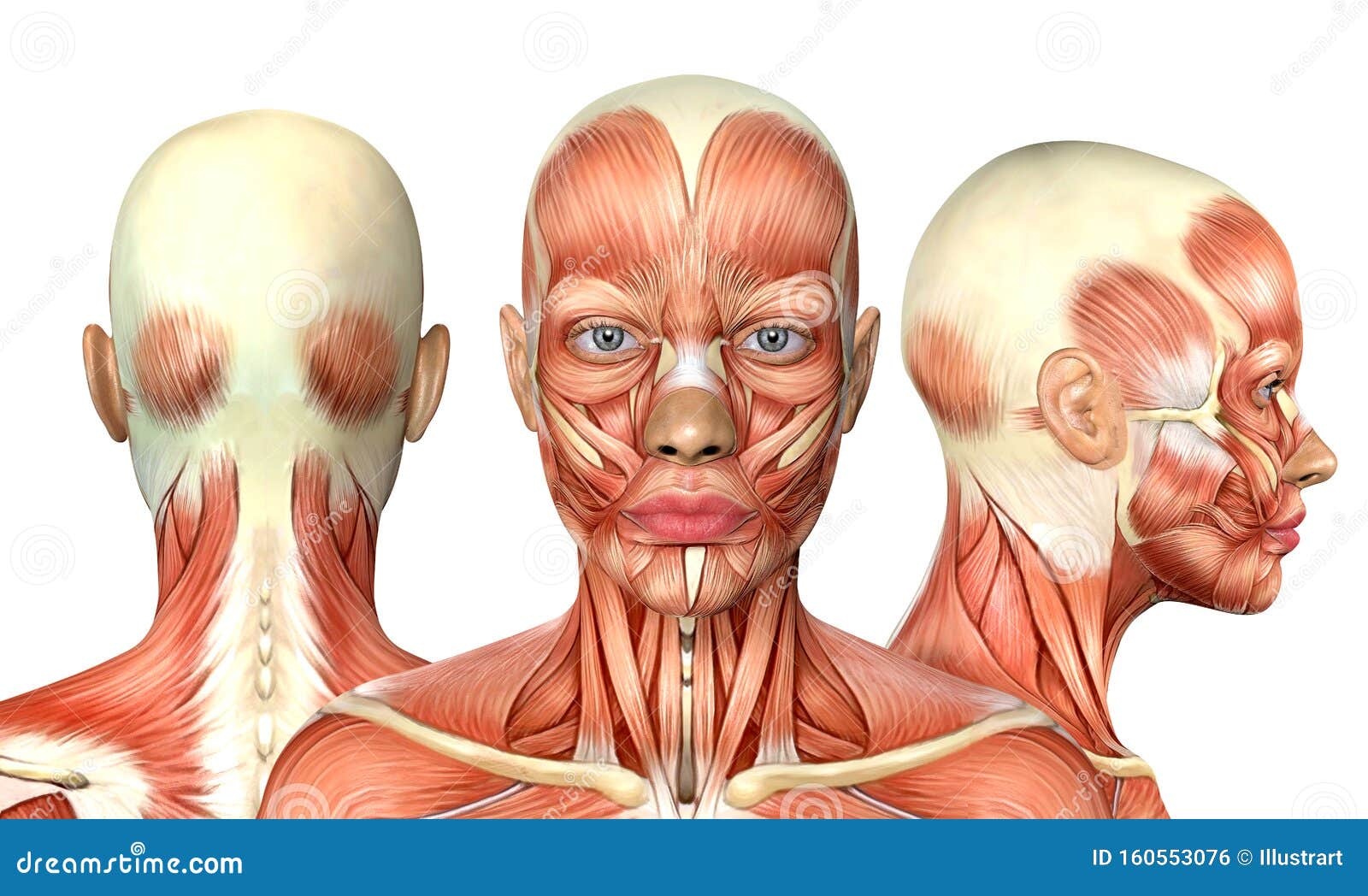


Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 48 771 Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
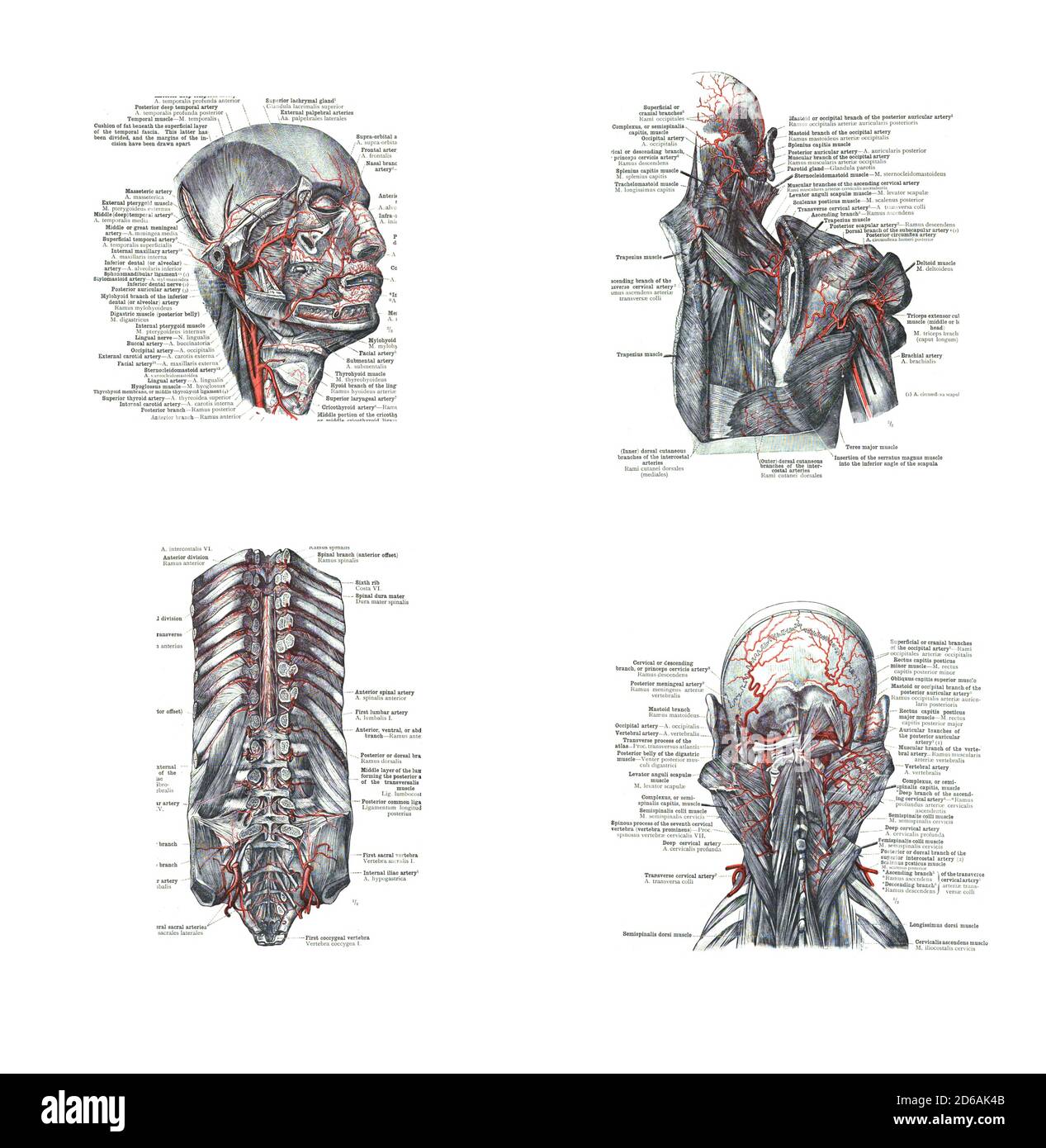


4 Views Of The Head Back And Spine From An Atlas Of Human Anatomy Carl Toldt 1904 Stock Photo Alamy



Human Head Artery And Vein Supplement Lateral View



Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock



Pin On Back To School



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Human Anatomy Openstax Cnx



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Human Anatomy Openstax Cnx



Back Of The Head Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Anatomyinsider
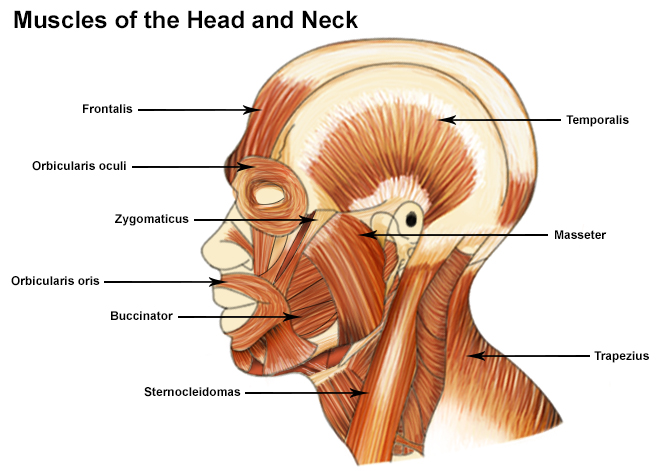


Seer Training Muscles Of The Head And Neck
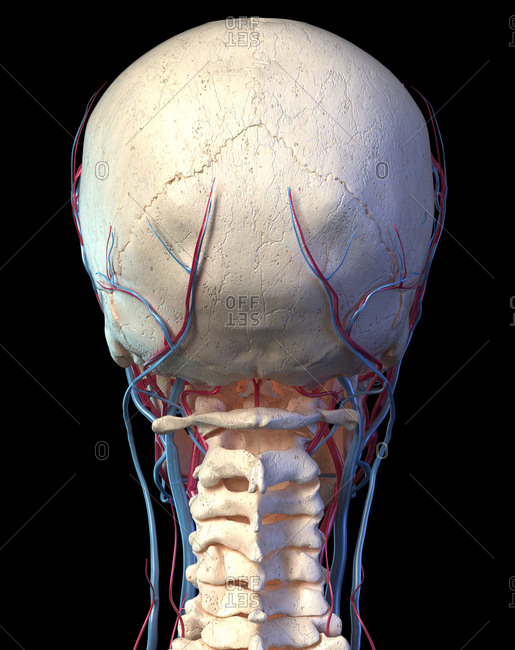


Vascular System Of The Human Head Viewed From The Back Computer 3d Rendering Artwork On Black Background Stock Photo Offset



50 421 Human Head Anatomy Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock



Human Head Skull And Cervical Vertebrae Rear View Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
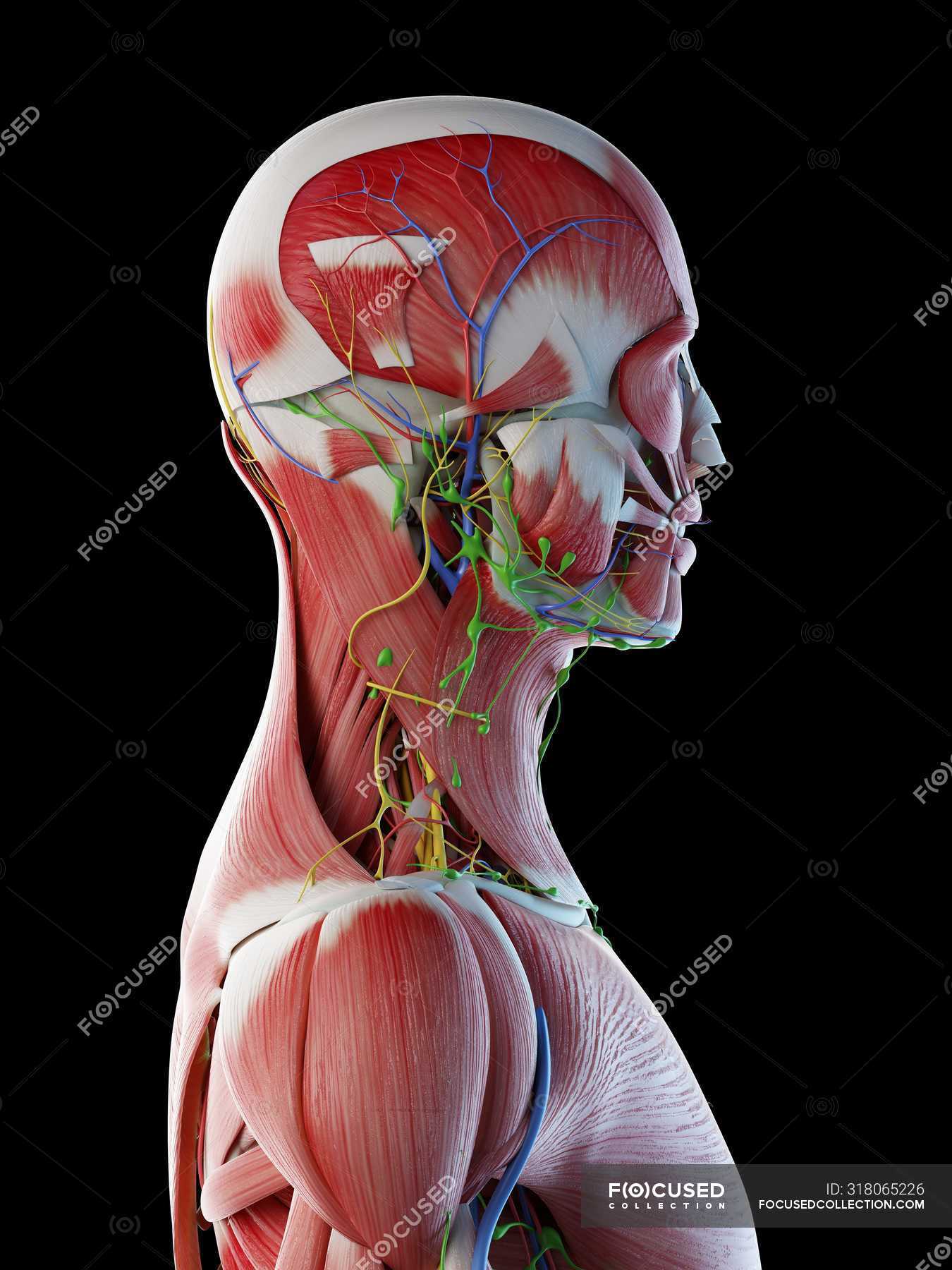


Male Anatomy Of Head Neck And Back With Musculature Computer Illustration Normal Transparent Stock Photo



Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck
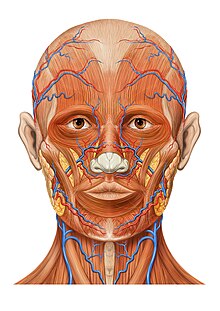


Human Head Wikipedia



Human Head Back View Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo C Anatomyinsider
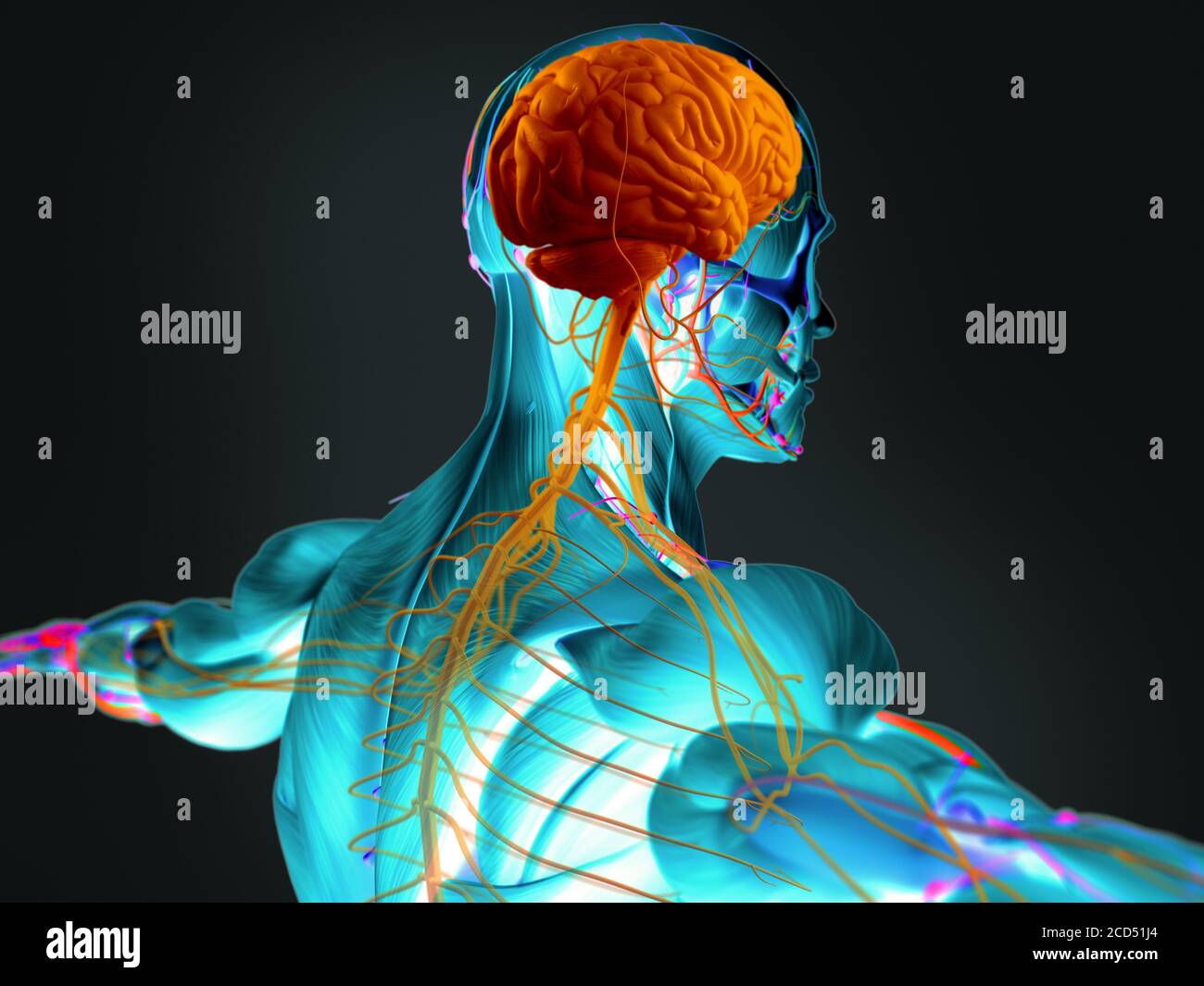


Human Anatomy 3d Futuristic Scan Technology With Xray Like View Of Human Body Back And Head And The Brain Vibrant Colors Xray Like Stock Photo Alamy



Human Anatomy Showing Back Full Body Stock Illustration



Muscular System Back Jpg 1492 2312 Human Body Anatomy Human Body Muscles Body Anatomy



The Human Muscle System Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscles Of The Neck Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14074/Back_muscles.png)


Back Muscles Anatomy And Functions Kenhub



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Human Anatomy Openstax Cnx



Human Anatomy Showing Back Full Body Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
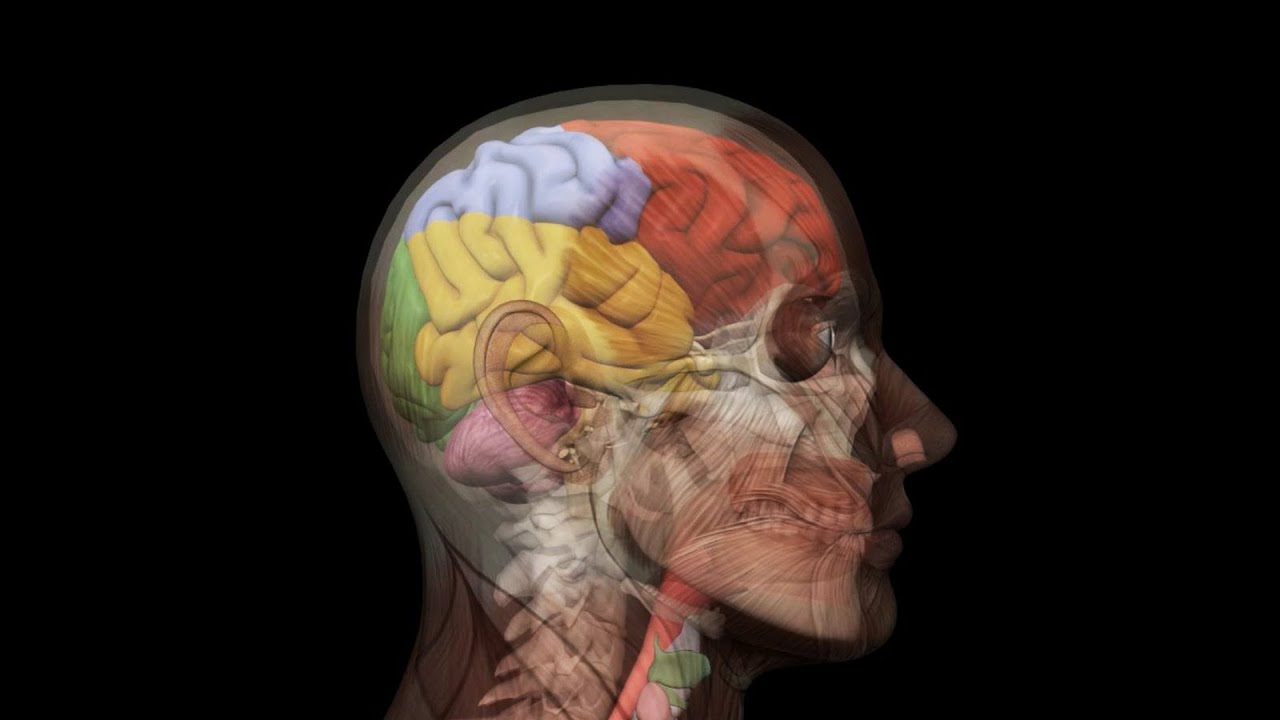


Human Head Anatomy 3d Model Loop Youtube



9 Muscles Of The Head And Jaw Motion Specific Release Youtube



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo Image By C Anatomyinsider



Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Images Page Everypixel
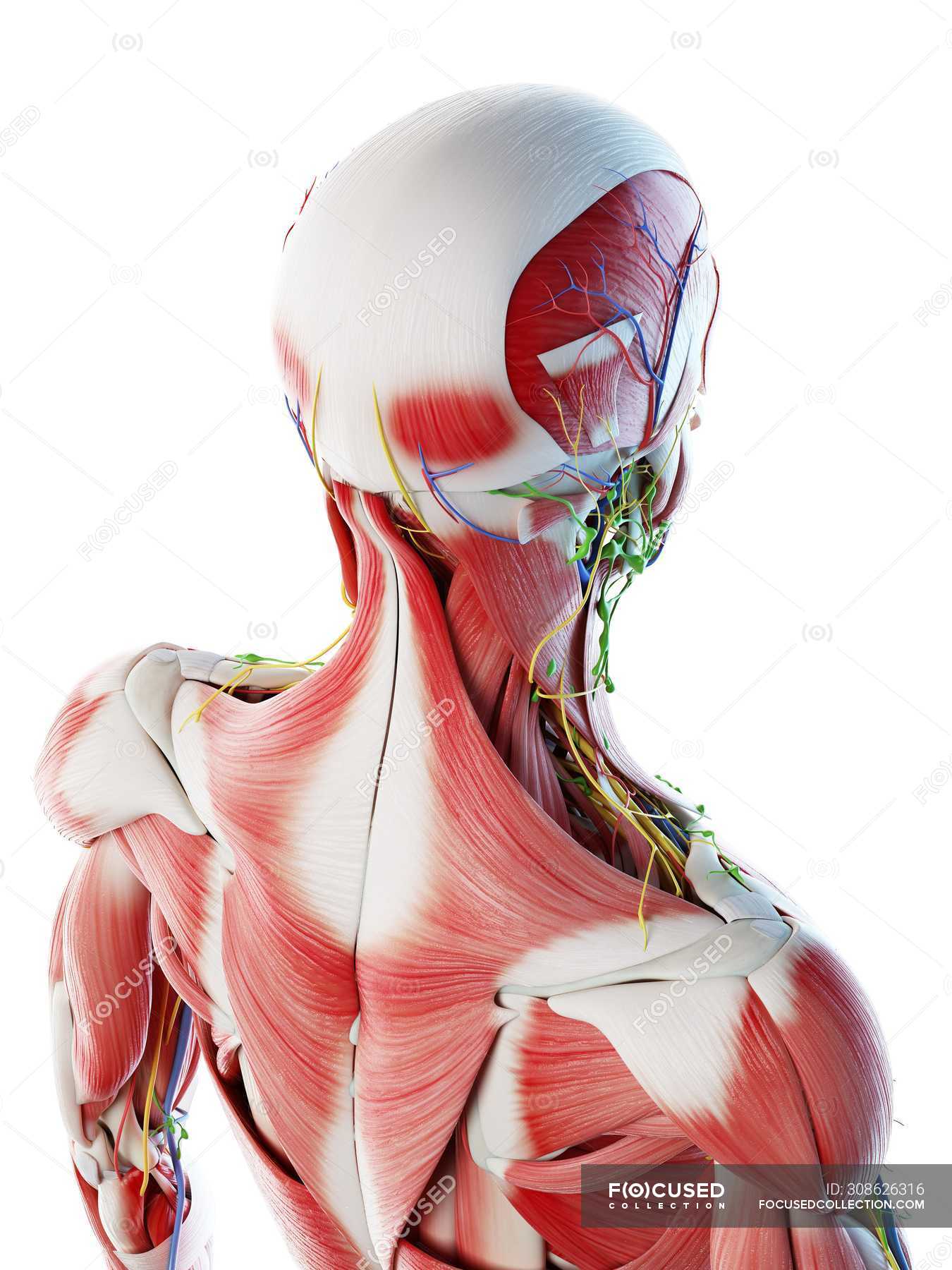


Male Back Neck And Head Muscles Computer Illustration Anatomical 3d Model Stock Photo


Stan Winston Studios Human Head Anatomy Sculpture Camera Ready Cosmetics



The Human Head Anatomy Class Allen Kathy Krueger Jennifer Allen Amazon Com Books



The Lymphatics Of The Head Face And Neck Human Anatomy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿